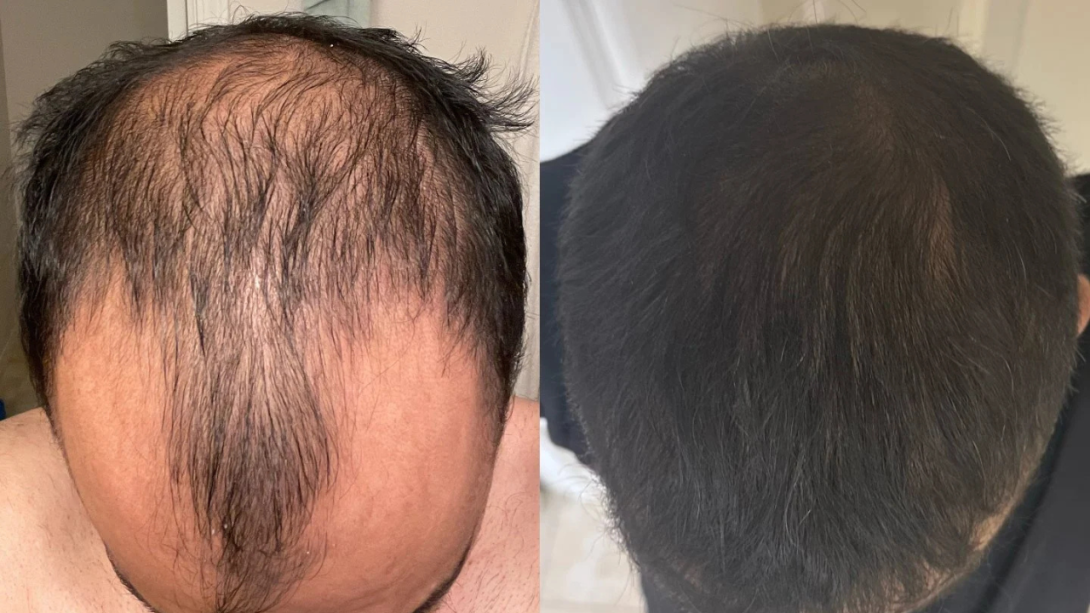
Introduction
Androgenetic Alopecia (AGA) is the most common form of hair loss in both men and women. Characterized by progressive miniaturization of terminal hairs into vellus hairs, AGA results in diffuse thinning and baldness due to shortened anagen phases and reduced follicular density. This article reviews the current medical treatments for AGA as outlined by Dr. Ratchathorn Panchaprateep of Chulalongkorn University in the article she published in PubMed, highlighting both FDA-approved options and emerging therapies.
Understanding Follicle Miniaturization
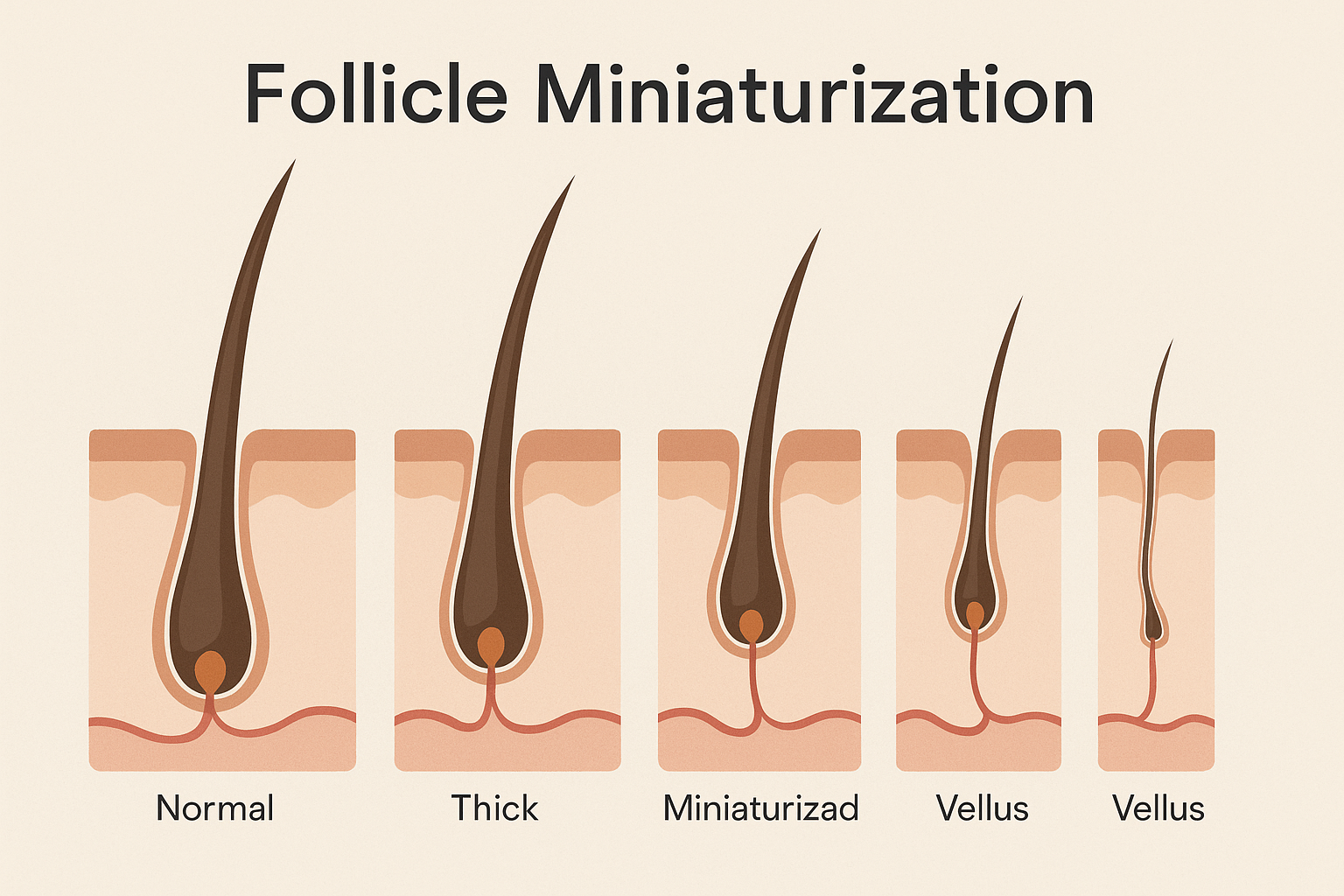
Hair loss in AGA is driven by genetics and androgens, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT binds to androgen receptors in hair follicles, leading to follicular shrinkage, shorter growth cycles, and eventual follicle dormancy. See below for a graphical representation of this process.
Topical Treatments: Minoxidil
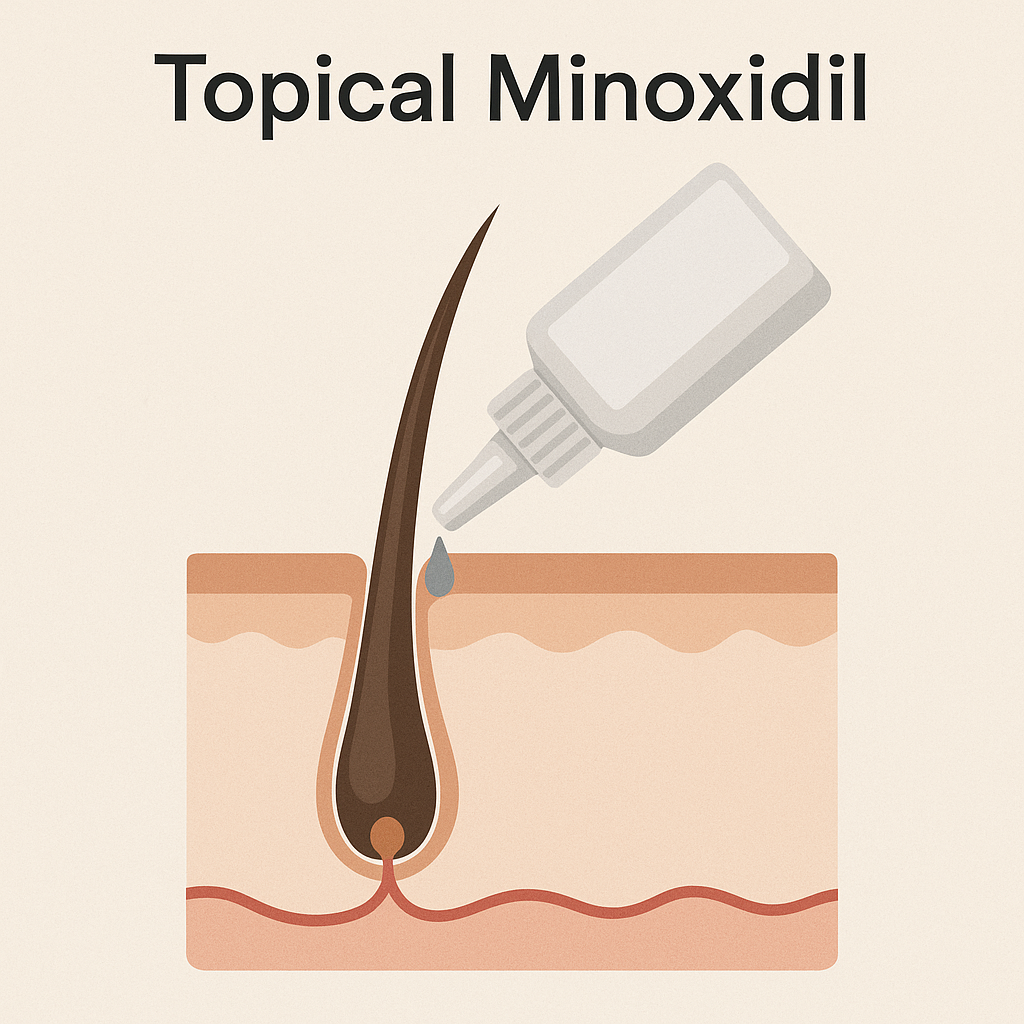
Minoxidil is a vasodilator that increases blood flow and upregulates VEGF, prolonging the anagen phase. Initially approved in 1988, it is available in 2% and 5% solutions and is applied directly to the scalp. Topical minoxidil effectively slows hair loss and promotes regrowth, especially in the early stages of AGA.
Oral Treatments: Finasteride and Dutasteride
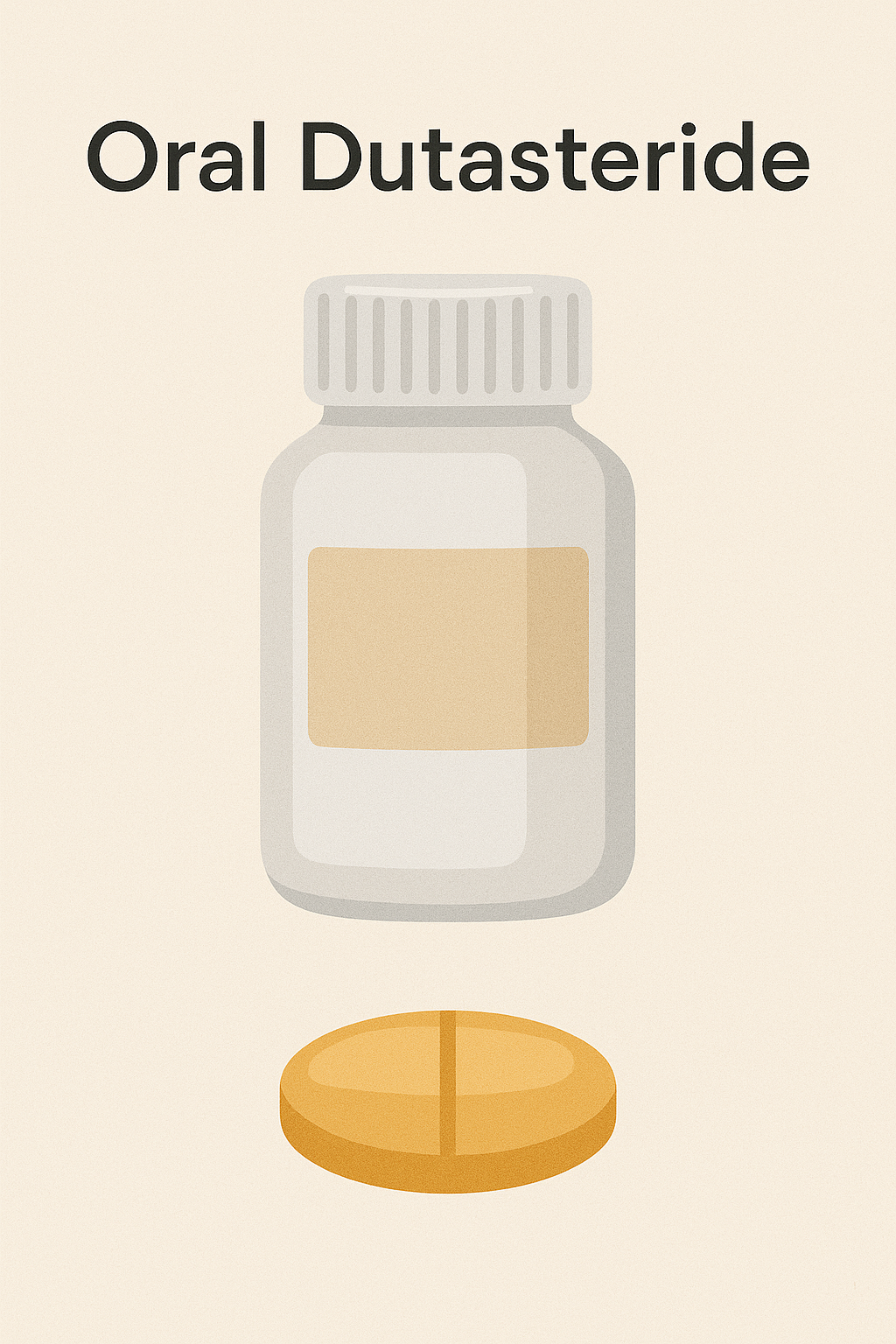

Finasteride is a type II 5-alpha reductase inhibitor that blocks the conversion of testosterone to DHT. At 1 mg daily, it significantly reduces scalp and serum DHT levels, improving hair density over time. Dutasteride, a dual type I and II 5-AR inhibitor, is even more potent, achieving up to 90% DHT reduction. Both drugs can lead to side effects like sexual dysfunction and mood changes, particularly in long-term use.
Emerging Treatments: Oral Minoxidil and PRP
![oral minoxidil and prp]](/sites/default/files/inline-images/32b6cf7b-aaf9-4267-9bd8-4f7c7513ca31.png)
Low-dose oral minoxidil (0.255 mg) has shown promise in both male and female AGA patients. It may offer more convenience and fewer cosmetic issues compared to its topical counterpart. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, involving injections of concentrated growth factors, is also gaining popularity. Clinical studies support its use in early-stage AGA for increased hair diameter and density.
Combination Therapies and Final Thoughts
Combination treatments can enhance outcomes, like topical minoxidil with finasteride or oral minoxidil with anti-androgens. Proper patient selection based on age, severity, and tolerance is critical. While medical treatments can be effective, they require consistency and time. Consulting with a qualified physician is essential for optimizing results.
Dr. Ratchathorn Panchaprateep