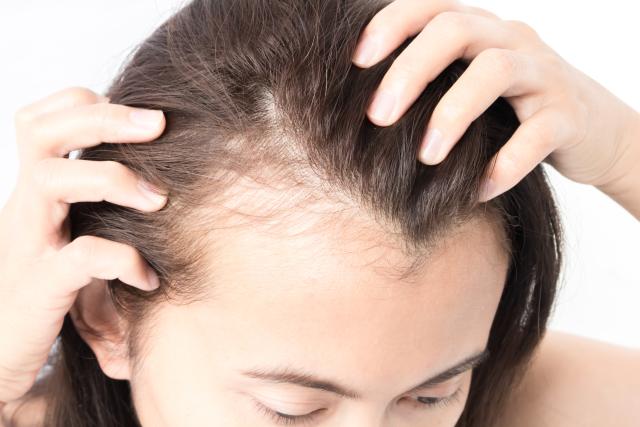
Female hair loss, otherwise known as Female Pattern Baldness (FPB), affects 1 out of every 4 women in the United States. Recent findings have found that the incidence of FPB has been reported to be as low as 8% and as high as 87%. And, it does appear to be as common for women as for men. Most often, menopause is the most frequent time for hair loss in women to become apparent.
For a woman to lose her hair can be even more troubling than for men. A woman with thinning hair is not generally accepted as part of the normal aging process. Society has come to expect a thick, luxurious head of hair as part of the attractiveness in women.
While males and females can both experience thinning hair, they typically do not lose their hair in the same order or appearance.
Women with thinning hair compared to Men
Typically men observe their hair loss earlier, whereas women will first notice it in their late 20's through their early 40's. Female Pattern Baldness (FPB) is often seen during hormonal changes. These include the use of birth control pills, following childbirth, or during or after the time of menopause.
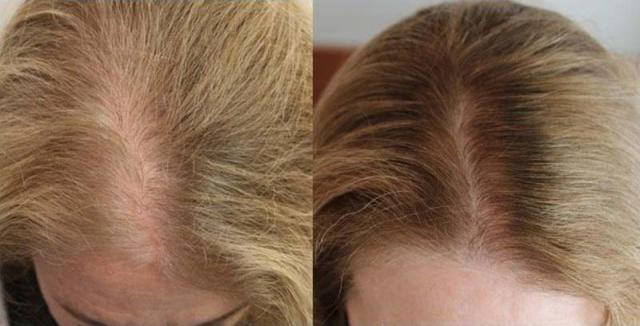
In addition, men typically have localized areas (patterns) of thinning, whilein women this usually occurs as thinning across the top, or over an even wider area. When women have very diffuse thinning over much of their scalp they are generally not good candidates for hair restoration surgery. However, women with localized hair loss, similar to the typical male pattern baldness, can successfully undergo hair restoration surgery.
Thinning hair in females is also characterized by an increase in the combination of normal thick hairs mixed in with finer, smaller hairs. This results in decreased density, and not total hair loss.
A woman's hair has also been proven to be more sensitive to the effects of stress than men's hair. Stress can result in hair loss in women and men. But this type of loss is not female pattern baldness. Rather, it is known as “telogen effluvium.” This type of hair loss is the shedding of hair in the resting phase when the body senses that it needs to divert its energies elsewhere. Therefore stress can temporarily changes the amount of hair that is shed. But the lost hair is likely to grow back.
The production of the hair loss-inducing androgens is also different among men and women. A woman produces a small quantity of androgens in the adrenal glands and the ovaries. The ovaries also produce pre-hormones, which are then converted to androgens on the outside of the ovaries or adrenal glands.
Generally speaking, a woman with hair loss will probably not experience total balding in a given area. But if there is total hair loss, this is most likely a sign of a previously hidden disease. For this reason, it’s important for females to have their hormone levels checked by a physician if they are experiencing heavy hair loss.
Finally, men and women react differently to various hair loss treatment options. In men, hair loss may be halted or even reversed by finasteride (brand named "Propecia"). However, Propecia is not safe for females or children. Minoxidil (Rogaine) can be effective for both men and women in treating hair loss.
However, for some women the causes of their hair loss are much more complex than the classic "male pattern baldness". Thus proper diagnosis of the underlying cause is vital before any hair loss treatments are attempted.
The following physicians are nationally well known experts in female hair loss. Feel free to contact them.
David Whiting in Dallas, Texas - 214 824-2087
Vera Price in San Francisco, California 415 353-4163
Maria Hordinsky in Minneapolis, Minnesota 612 625-1493
Wilma Bergfeld in Cleveland, Ohio 216 444-5722
For a web community that is dedicated to female hair loss visit HerAlopecia.com