Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping nearly every branch of medicine—and hair restoration is no exception. One of the most exciting advances is Scalp Scan AI, an imaging-based diagnostic system that uses machine learning to assess hair loss severity, donor supply, and overall scalp health.
This article explores the technology behind scalp scan AI, its clinical relevance, and how it is transforming hair restoration surgery by enabling more precise diagnosis, better treatment planning, and patient education.
What Is Scalp Scan AI?
Scalp Scan AI uses high-resolution scalp imaging and machine learning algorithms to analyze follicular density, miniaturization, and donor zone stability.
It measures:
- Hair density (hairs/cm²)
- Follicular unit (FU) grouping
- Percentage of miniaturized (vellus-like) hairs
- Number of empty follicles
- Hair shaft diameter variability
- Scalp inflammation or scarring patterns
AI transforms this data into actionable insights for both patients and physicians.
The Science Behind It: How It Works
The process typically includes four main stages:
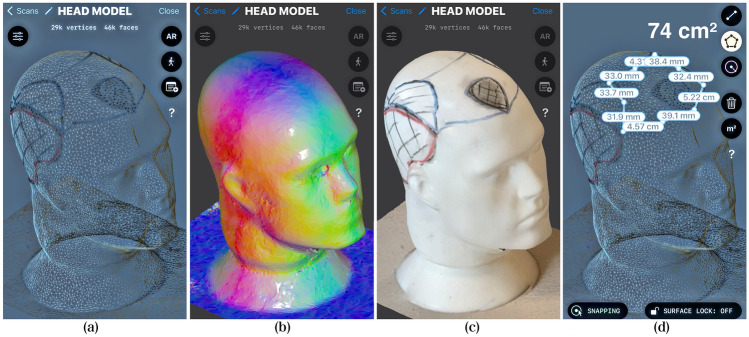
Figure 1: Scalp Scan AI Workflow
- Image Capture
Specialized dermatoscopic cameras or digital trichoscopes capture high-magnification scalp images under polarized light. - Image Preprocessing
The system applies computer vision techniques—like noise reduction, contrast normalization, and edge detection—to isolate hair shafts and follicles. - Model Analysis (AI Inference)
Using convolutional neural networks (CNNs), the AI identifies patterns indicative of miniaturization, healthy growth, or scarring. - Diagnostic Output
The algorithm returns a prediction, such as “mild AGA” or “advanced thinning,” along with confidence scores and treatment recommendations.
Quantifying Hair Loss with Trichoscopic Parameters
Recent scientific literature, including the PRECISE Scale developed by Pittella et al. (2024), has demonstrated how trichoscopic parameters can be modeled using Support Vector Machines (SVMs) to classify hair loss severity.
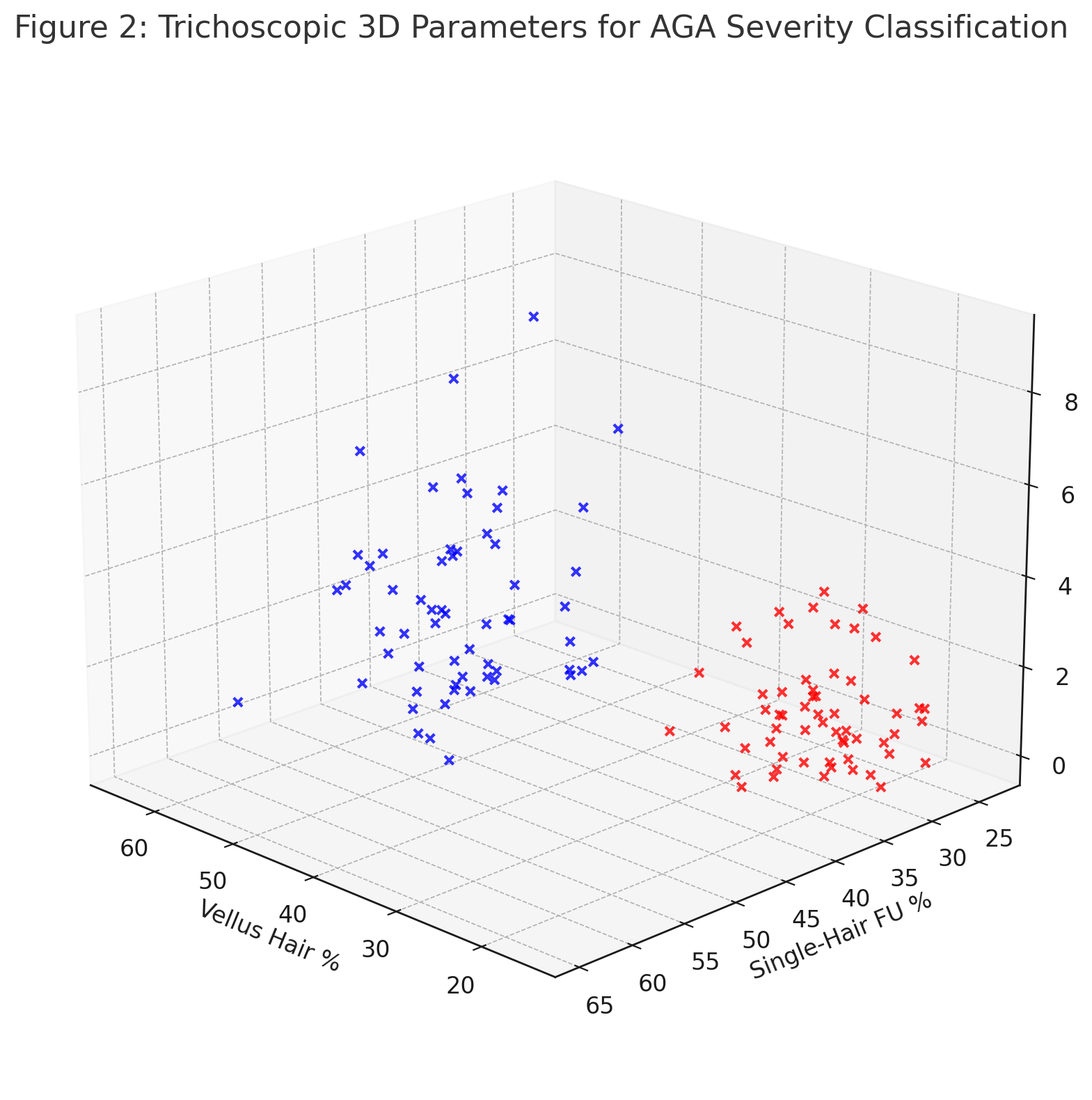
Figure 2: 3D representation of vellus hair percentage, single-hair follicular units, and empty follicles—separating mild from moderate-severe androgenetic alopecia.
Key Metrics Used:
Parameter
Normal Range
Severe AGA Indicator
Vellus hair %
< 15%
> 30%
Single-hair FU %
< 25%
> 40%
Empty follicles (count)
0–1
≥ 2
Predicting Severity: AI Confidence Scores
Instead of binary “yes/no” outputs, Scalp Scan AI generates probability scores—providing physicians with a quantitative basis for clinical decision-making.
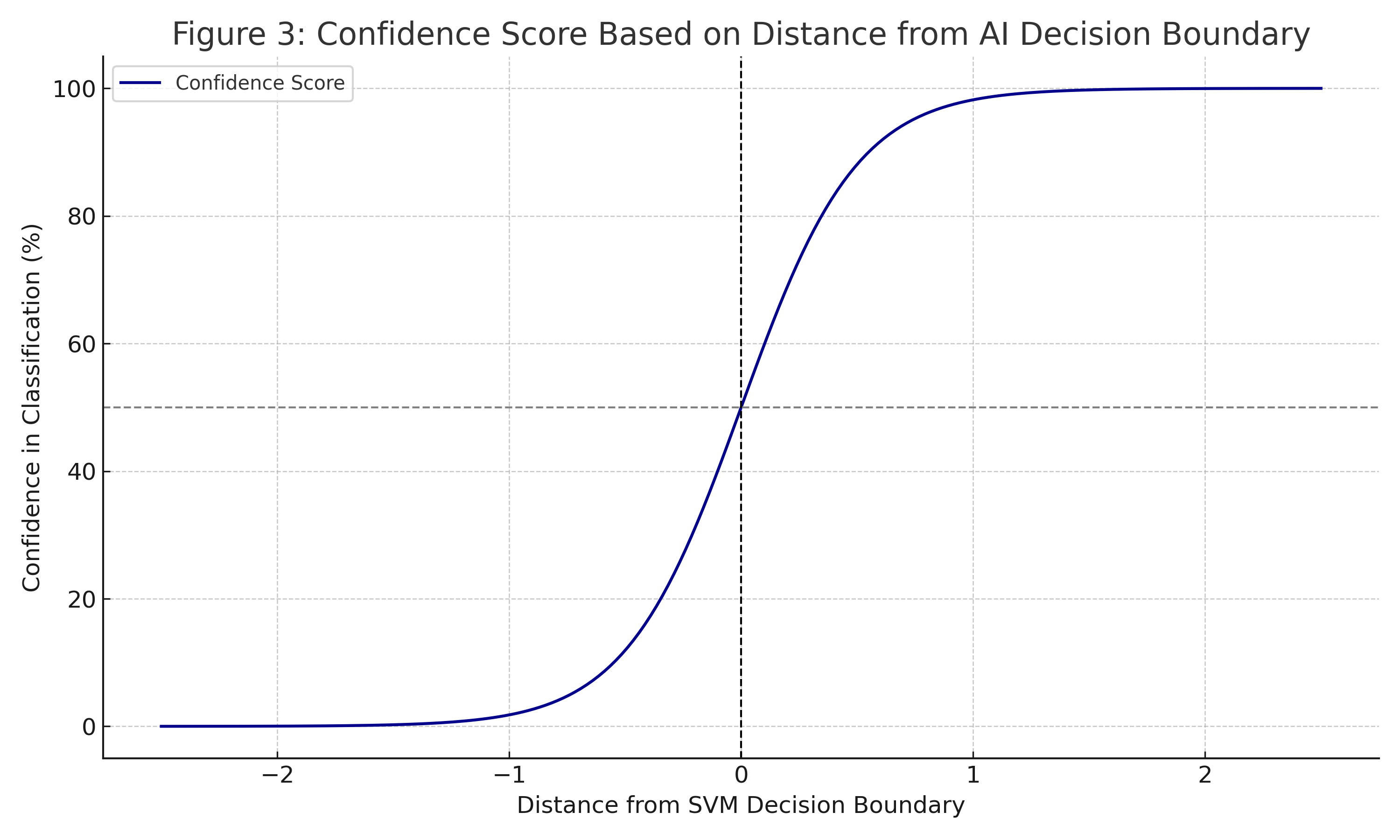
Figure 3: Confidence score based on the distance from the AI decision boundary. Greater distances indicate stronger classification confidence.
This feature is handy for borderline cases, where visual inspection alone might not be enough.
Real-World Application: A Diagnostic Workflow
Let’s walk through a hypothetical patient example:
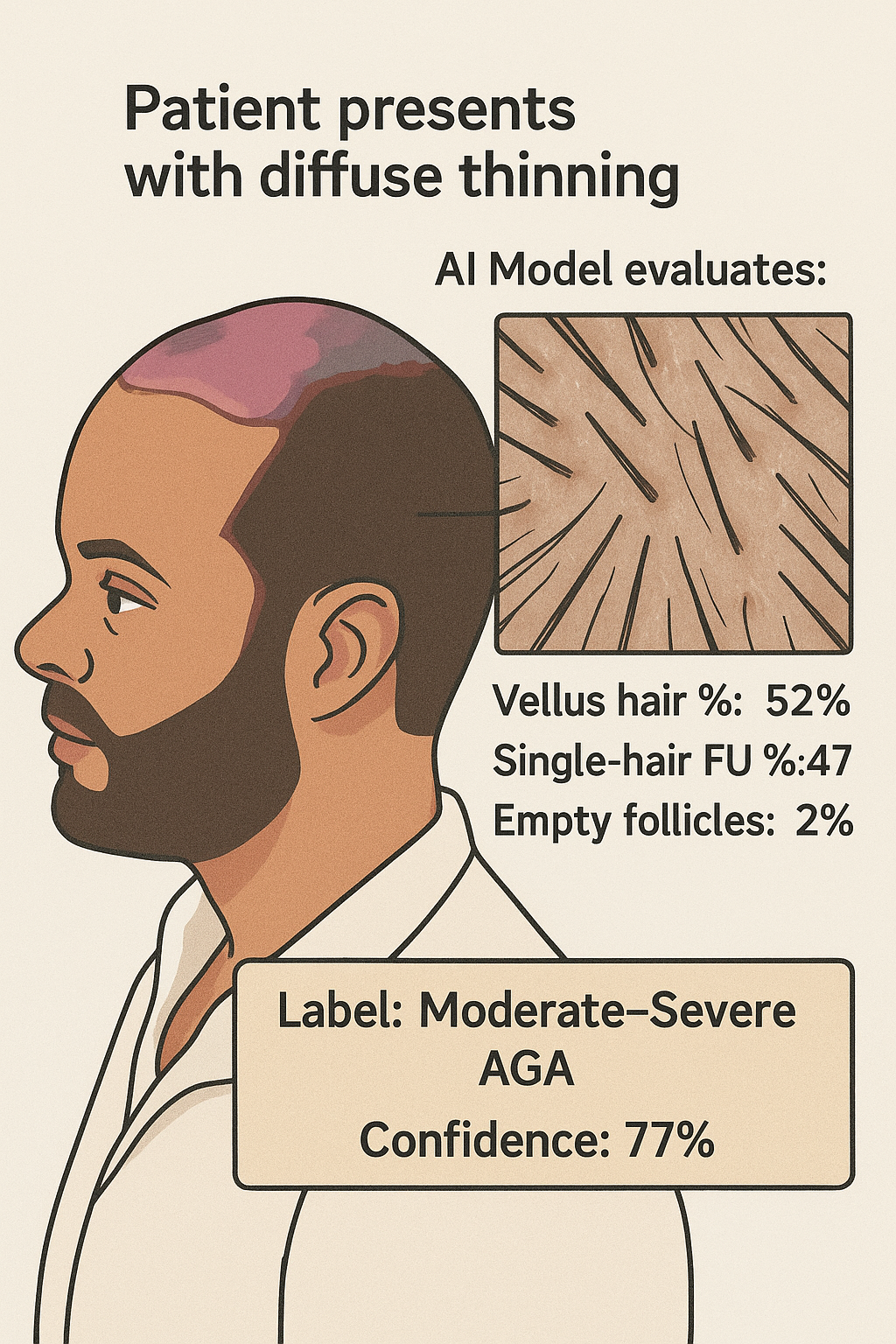
Figure 4: From image capture to AI-based diagnosis in a real-world clinical setting.
Step-by-step:
- Patient presents with diffuse thinning
- Trichoscopic imaging conducted
- AI model evaluates:
- Vellus hair %: 52%
- Single-hair FU %: 47%
- Empty follicles: 2
- AI Output:
- Label: Moderate–Severe AGA
- Confidence: 77%
This kind of structured, quantitative data provides both patients and doctors with clarity, enabling better treatment adherence and trust in medical decisions.
Benefits for Hair Transplant Surgery
1. Improved Candidate Selection
Scalp Scan AI can help identify patients with conditions like DUPA (Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia), which disqualifies them from surgery due to donor instability.
2. Accurate Donor Zone Assessment
Traditional donor assessments relied heavily on clinical observation. AI now allows surgeons to measure donor density, graft availability, and miniaturization risks with precision.
3. Objective Progress Tracking
Patients undergoing finasteride, minoxidil, or PRP therapy can visually track their response over time using scalp scans.
4. Graft Planning & Distribution
AI-generated follicular maps guide surgeons in extracting and placing grafts more strategically.
Limitations and Ethical Concerns
No technology is without limitations:
- Data Bias: AI models need diverse training data. A model trained primarily on lighter skin tones or straight hair types may perform poorly on others.
- Overreliance: Physicians must remember AI is a support tool, not a replacement for clinical judgment.
- Privacy: Scalp images and metadata must comply with HIPAA/GDPR data handling protocols.
The Future of AI in Hair Restoration
What lies ahead?
- 3D Mapping: AI can soon reconstruct scalp topography for even more accurate graft distribution.
- Remote Diagnostics: Smartphone-based trichoscopy may allow patients to scan from home.
- Predictive Models: Algorithms could forecast hair loss progression based on genetics, lifestyle, and treatment compliance.
Conclusion: Human + Machine = Precision Medicine
Scalp Scan AI marks a new era in personalized hair restoration. It provides:
- Standardized diagnostics
- Predictive analytics
- Enhanced treatment precision
- Better patient engagement
But its actual value comes when it complements—not replaces—an experienced hair restoration surgeon.
Want to See It in Action?
Join the Hair Restoration Network to view real-world patient journeys, scalp scan results, and experiences with AI-assisted diagnostics.
Dr. Felipe Pittella


